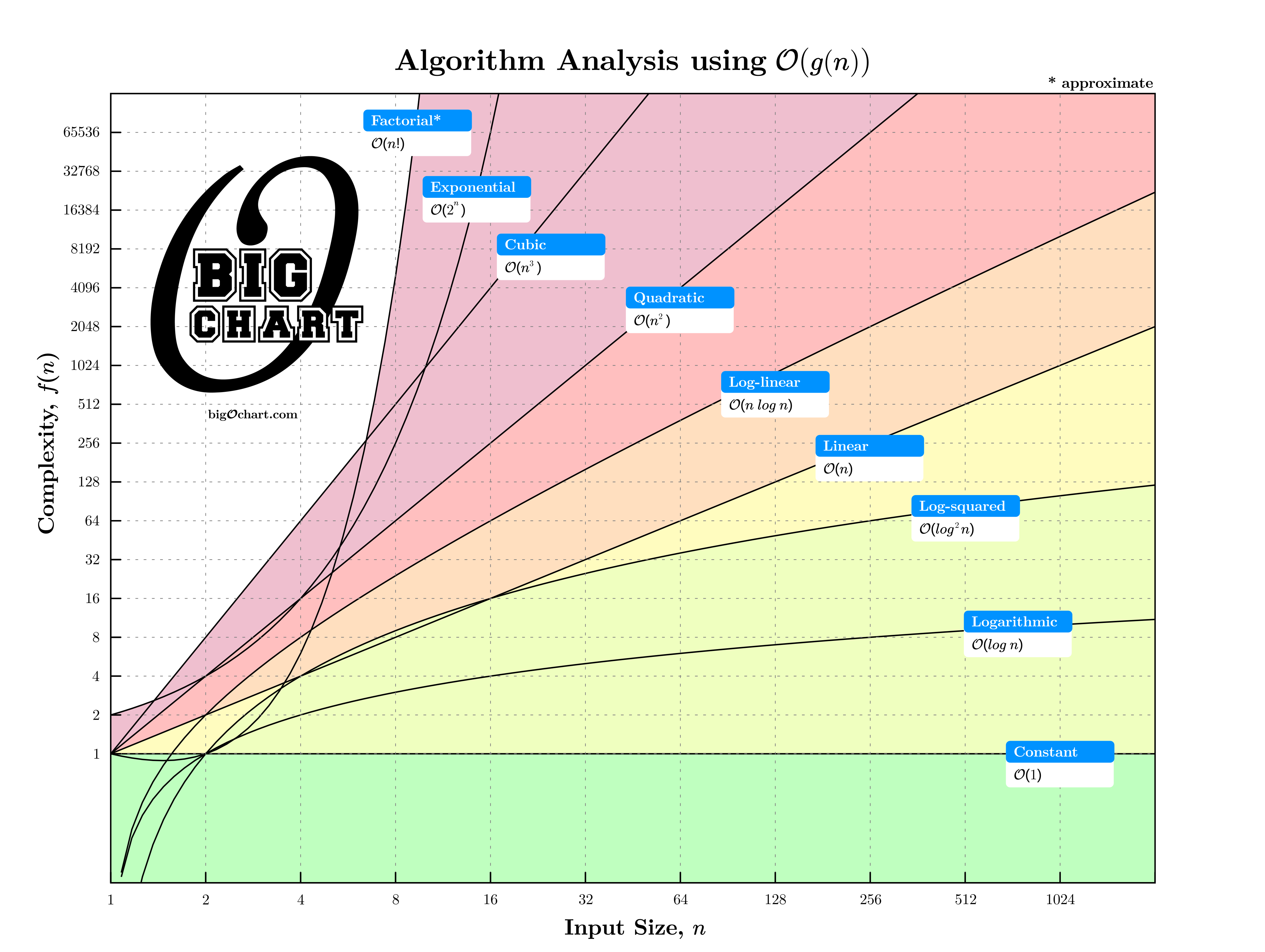
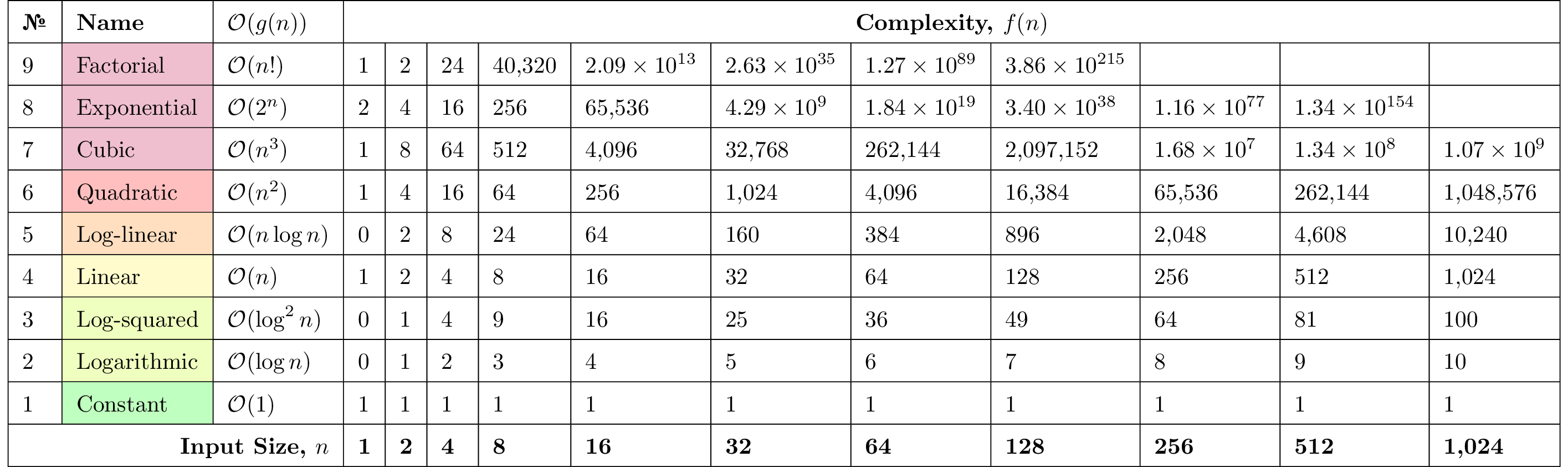
Figure 1: \(\mathcal{O}\)-notation, a.k.a. "Big-O", is used to express the asymptotic upper bound on \(f(n)\) by some constant multiple of \(g(n)\), written as \(f(n) = \mathcal{O}(g(n))\). This upper bound represents the growth of the worst case running time or space consumption and makes no claims regarding tightness of fit. The shaded area underneath each function depicts the absence of an asymptotic lower bound associated with \(\mathcal{O}\)-notation. See Table 1 for a partial numerical analysis.